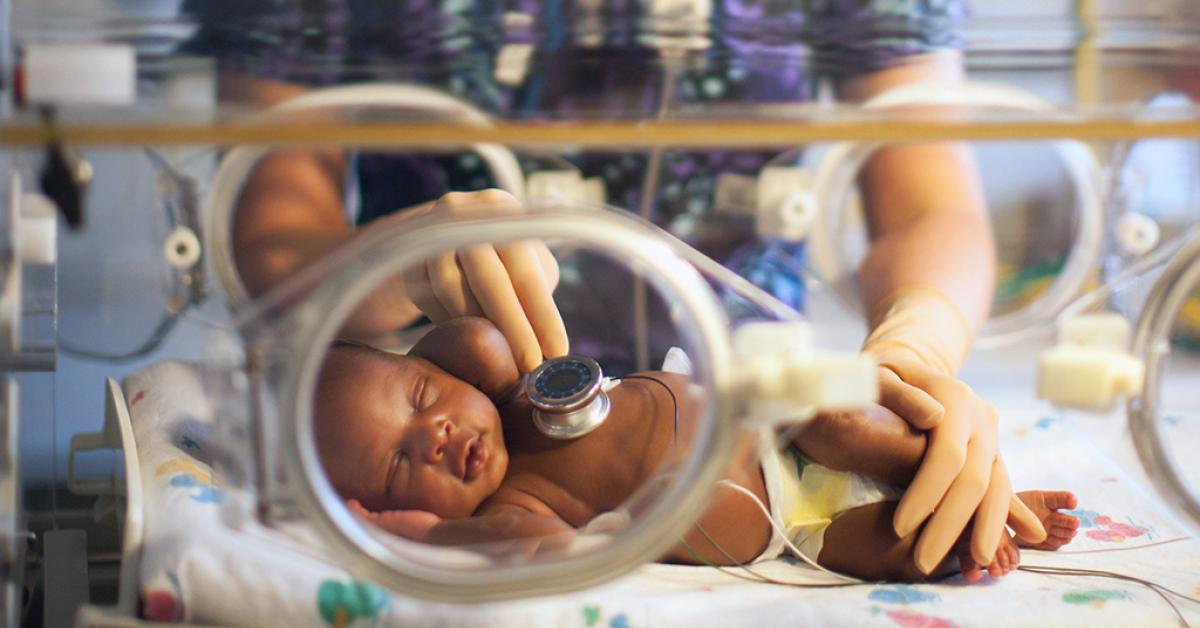
The birth of a newborn is a momentous occasion, but for some families, it comes with unexpected challenges. Premature births or health complications may necessitate specialized care in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). Central to this care is the use of incubators, providing a controlled environment crucial for the survival and development of these vulnerable infants.
What is Neonatal and NICU Care?
Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of a newborn’s life-a critical period requiring meticulous care, especially for premature or ill infants. The NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit) is a specialized hospital unit equipped to provide intensive medical attention to these newborns.
The Role of Incubators in Newborn Care
An incubator is a vital apparatus in the NICU, designed to maintain optimal temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels for newborns who cannot regulate these on their own. It shields infants from infections and external disturbances, ensuring a stable environment for growth and recovery .
Levels of Neonatal Care
Neonatal care is stratified into four levels, each catering to specific needs:
- Level I (Basic Newborn Care): For healthy newborns requiring routine care.
- Level II (Special Care Nursery): Caters to infants born at or after 32 weeks gestation, needing moderate care such as feeding assistance or short-term respiratory support.
- Level III (NICU): Provides comprehensive care for very premature or critically ill newborns, including advanced respiratory support and access to pediatric subspecialists.
- Level IV (Regional NICU): Offers the highest level of neonatal care, including surgical interventions and treatment for complex conditions.
ICU vs. NICU:
While both are intensive care units, their patient demographics and care focus differ:
- ICU (Intensive Care Unit): Primarily for critically ill adults and older children.
- NICU: Specialized for newborns, particularly those born prematurely or with serious health issues.
Finding Hospitals with NICU Facilities
For parents seeking hospitals with NICU near you, it’s essential to:
- Consult with obstetricians or pediatricians for referrals.
- Research hospital websites for information on their neonatal care levels.
- Consider proximity and the hospital’s capabilities in handling specific neonatal conditions.
FAQs
- What is the full form of NICU in medical terms?
- NICU stands for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.
- Why might a newborn need an incubator?
- To maintain body temperature, provide a sterile environment, and support underdeveloped organs.
- How long do babies stay in the NICU?
- Duration varies based on the baby’s condition, ranging from days to several weeks or months.
- Can parents visit their baby in the NICU?
- Yes, most NICUs encourage parental involvement, with specific visiting hours and guidelines.
- What are the levels of neonatal care?
- Levels I to IV, with increasing complexity and specialization of care.
- How does NICU care differ from ICU care?
- NICU is specialized for newborns, while ICU caters to critically ill patients of all ages.
- Are NICU services available in all hospitals?
- Not all hospitals have NICUs; availability depends on the facility’s resources and specialization.
- What is the survival rate for premature babies in the NICU?
- Survival rates have improved significantly, especially with advanced NICU care, but vary based on gestational age and health conditions.
- What support is available for parents with babies in the NICU?
- Hospitals often provide counseling, support groups, and resources to assist families during this challenging time.
- Can a baby go home directly from the NICU?
- Yes, once the baby meets specific health criteria, they can be discharged home.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for medical guidance specific to your situation.