What Are Hemorrhoids?
- Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus.
- They can cause pain, itching, bleeding, and discomfort during bowel movements.
- Hemorrhoids are common, affecting nearly half of adults by age 50.
Why Is Hemorrhoid Grading Important?
- Helps determine severity and appropriate treatment.
- Guides doctors in deciding between home remedies, medical procedures, or surgery.
- Enables patients to understand their condition better.
Hemorrhoid Types and Locations
| Type | Location | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Hemorrhoids | Inside the rectum | Usually painless, may bleed |
| External Hemorrhoids | Around the anus | Painful swelling, itching, discomfort |
| Thrombosed Hemorrhoids | External with blood clot | Severe pain, swelling |
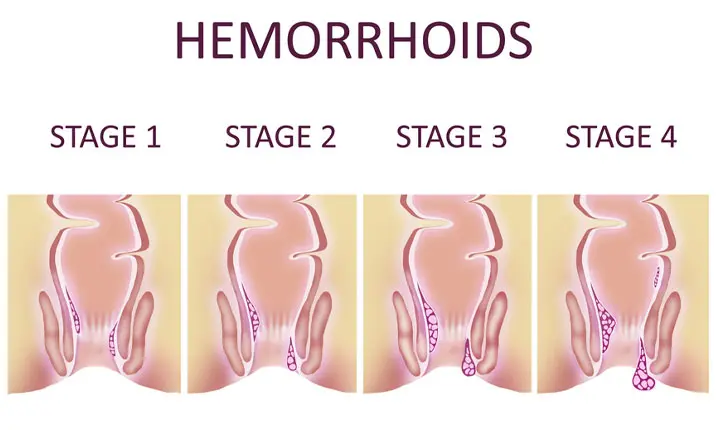
Hemorrhoid Grading System Explained
Hemorrhoids are typically graded based on their size and prolapse (protrusion) outside the anal canal.
| Grade | Description | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I | No prolapse; hemorrhoids remain inside the anus | Occasional bleeding, mild discomfort | Dietary changes, topical creams |
| Grade II | Prolapse during bowel movements but spontaneously reduce | Bleeding, itching, mild pain | Lifestyle changes, rubber band ligation |
| Grade III | Prolapse during bowel movements and must be manually pushed back | Bleeding, pain, swelling | Minimally invasive procedures, surgery if needed |
| Grade IV | Prolapsed and cannot be manually reduced, may become thrombosed | Severe pain, bleeding, possible complications | Surgery required |

Hemorrhoid Size Chart
| Grade | Approximate Size (mm) | Visual Description |
|---|---|---|
| I | < 5 mm | Small swelling inside anus |
| II | 5 – 10 mm | Protrudes temporarily outside anus |
| III | 10 – 20 mm | Larger prolapse requiring manual reduction |
| IV | > 20 mm | Large prolapse, permanently outside |
Signs and Symptoms by Hemorrhoid Grade
- Grade I: Mild itching, occasional bright red blood on toilet paper.
- Grade II: Increased bleeding, discomfort during bowel movements.
- Grade III: Noticeable lump outside anus, pain during sitting or defecation.
- Grade IV: Persistent pain, swelling, difficulty cleaning, possible infection.
Causes and Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Straining during bowel movements
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Low fiber diet
- Aging (loss of tissue elasticity)
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoid Grade
- Visual examination by proctologist.
- Digital rectal examination.
- Anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to view internal hemorrhoids.
- Patient history and symptom description.
Treatment Options Based on Hemorrhoid Grade
| Grade | Non-Surgical Treatments | Surgical Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| I | High-fiber diet, stool softeners, sitz baths, creams | Rarely needed |
| II | Rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, infrared coagulation | Surgery in rare persistent cases |
| III | Minimally invasive procedures (ligation, coagulation) | Hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy |
| IV | Surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy) | Surgery is usually mandatory |
Prevention Tips for Hemorrhoids
- Increase fiber intake (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid straining during bowel movements
- Exercise regularly to improve bowel function
- Avoid sitting for long periods
- Use the bathroom as soon as the urge occurs
When to See a Doctor?
- Persistent bleeding or pain
- Prolapsed hemorrhoids that do not reduce
- Signs of infection (fever, severe pain, swelling)
- Sudden change in bowel habits or unexplained weight loss
FAQs on Hemorrhoids Grading and Size
Q1: Can hemorrhoids shrink on their own?
- Yes, Grade I and II hemorrhoids often improve with lifestyle changes.
Q2: How long does it take to recover from hemorrhoid surgery?
- Recovery usually takes 2-4 weeks depending on the procedure.
Q3: Are large hemorrhoids more dangerous?
- Larger prolapsed hemorrhoids can cause more pain and complications if untreated.
Q4: Can hemorrhoids cause cancer?
- No, hemorrhoids are benign but symptoms like bleeding should be evaluated to rule out other conditions.
Summary Table: Hemorrhoids Grading & Treatment Overview
| Grade | Size | Prolapse Type | Symptoms | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | < 5 mm | No prolapse | Mild discomfort, bleeding | Diet, topical treatment |
| II | 5-10 mm | Prolapse, reduces spontaneously | Bleeding, mild pain | Non-surgical procedures |
| III | 10-20 mm | Prolapse, manual reduction | Pain, swelling | Minimally invasive surgery |
| IV | > 20 mm | Prolapse, no reduction | Severe pain, complications | Surgery |
Final Thoughts
Understanding hemorrhoid grading and size helps in effective treatment and faster recovery. Early intervention can prevent progression to severe grades, reducing discomfort and the need for surgery.
If you experience symptoms consistent with hemorrhoids, consult a healthcare professional to get an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Disclaimer: This content is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment of hemorrhoids or any other medical condition.
References:
- American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. https://fascrs.org
- Mayo Clinic – Hemorrhoids Overview. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids
- Cleveland Clinic – Hemorrhoid Grades. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10338-hemorrhoids